PE coated paper is one of the most widely used functional paper materials in the global packaging industry. It combines the natural strength, stiffness, and printability of paper with the moisture resistance and heat-sealing capability of polyethylene (PE). Because of its balanced performance, cost efficiency, and mature manufacturing technology, PE coated paper has become a standard material choice for food service packaging, disposable containers, and protective paper applications.
This article explains what PE coated paper is, how it is manufactured, its key benefits, typical applications, critical technical specifications to review with suppliers, and the limitations and risks that engineers and procurement teams should understand before sourcing.
Quick Definition
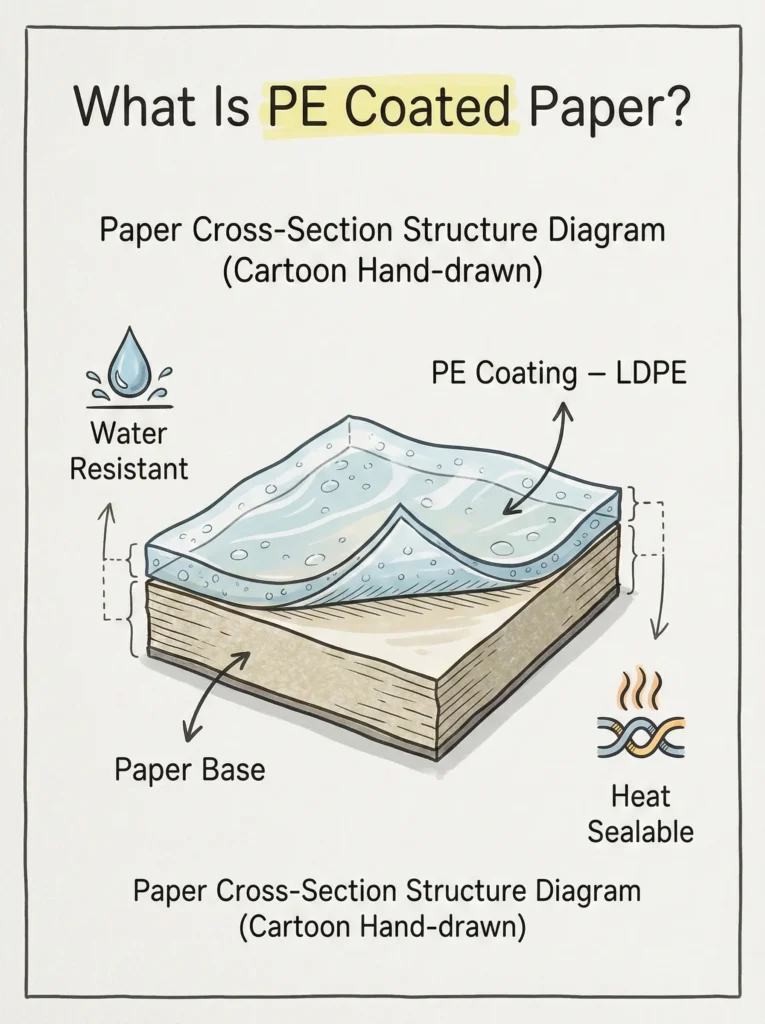
PE coated paper = paper substrate + polyethylene extrusion coating layer
In most commercial applications, the coating material is LDPE (low-density polyethylene), applied to the paper surface through an extrusion coating process. The PE layer forms a continuous, non-porous film that provides:
· Water and moisture resistance
· Basic grease resistance
· Heat sealability
· Improved surface integrity
The paper substrate contributes stiffness, structural strength, and printability, while the PE layer delivers functional barrier and sealing properties. This combination makes PE coated paper suitable for direct food contact packaging under controlled conditions.
How It’s Made
Extrusion Coating Process
PE coated paper is produced using an extrusion coating line, a continuous industrial process widely used in paper and packaging manufacturing.
The basic process flow includes:
· Melting – PE resin pellets are heated until fully molten
· Extrusion – molten PE is extruded through a flat die
· Coating – the molten PE is applied evenly onto the moving paper web
· Cooling – a chill roll rapidly cools and solidifies the PE layer
· Rewinding – the finished PE coated paper is wound into rolls
During extrusion, the molten PE partially penetrates the surface pores of the paper, creating mechanical anchoring. This results in strong adhesion without the need for separate adhesives.
Single-Side vs Double-Side PE Coating
Single-side PE coated paper
Used when barrier or heat sealability is required on only one surface, such as paper cups or food liners.
Double-side PE coated paper
Provides improved moisture protection and structural stability. Common in paper bowls, soup containers, and liquid packaging where both internal and external moisture exposure occurs.
The choice depends on application requirements, cost targets, and converting processes.
Key Benefits
PE coated paper remains popular because it offers a reliable balance between performance and cost.
Water and Moisture Resistance
The PE layer forms an effective moisture barrier, preventing liquid absorption and fiber swelling. This is essential for packaging hot or cold beverages and moist foods.
Excellent Heat Sealability
LDPE softens and melts within a well-defined temperature range, enabling consistent heat sealing during cup forming, box sealing, or pouch production.
Cost-Effective Solution
Compared to multi-layer laminates or high-barrier films, PE coated paper is relatively economical, especially for high-volume applications.
Wide Application Compatibility
PE coated paper works well with common printing, die-cutting, forming, and sealing equipment, making it easy to integrate into existing production lines.

Typical Uses
Because of its versatility, PE coated paper is used across many food service and packaging applications.
Single- or double-side PE coated cup stock paper is the industry standard for hot and cold beverage containers.
Takeaway Food Boxes
Used for fast food, bakery items, and ready-to-eat meals where moisture resistance and heat sealing are required.
Food Packaging Liners
PE coated paper is often used as an inner liner for paper bags or cartons to protect against moisture and light grease exposure.
These applications rely on PE coated paper’s ability to maintain structural integrity under short-term liquid or moisture contact.
Key Specs to Ask Suppliers
Paper Basis Weight (GSM)
Defines stiffness and mechanical strength. Higher GSM generally improves rigidity but increases cost.
PE Coating Weight / Thickness
Measured in g/m² or microns (μm). Thicker coatings improve barrier and sealing performance but negatively impact recyclability.
Heat Seal Temperature Range
Includes heat seal initiation temperature (SIT) and optimal sealing window. This is critical for stable production performance.
Odor and Migration Declarations
Suppliers should provide food-contact compliance statements addressing odor neutrality, additive safety, and migration risk.
Reliable documentation builds trust and reduces downstream regulatory and quality risks.

Limitations & Risks
Despite its advantages, PE coated paper has well-defined limitations that should be evaluated realistically.
Recycling Challenges
Paper-plastic composites are difficult to recycle because separating PE from paper fibers requires specialized infrastructure. Many recycling systems treat PE coated paper as mixed waste.
Heat Resistance Limitations
LDPE has a relatively low melting point. PE coated paper is not suitable for oven use and may deform under prolonged high-temperature exposure.
Limited Grease Barrier
While PE provides basic grease resistance, it is not a high-performance oil barrier. For high-fat or long-contact applications, multi-layer laminates or additional barrier layers may be required.
Understanding these constraints helps prevent over-specification or incorrect material selection.
Conclusion
PE coated paper is a mature, proven material solution that continues to play a central role in food service and packaging industries. Its success lies in its simple structure, stable manufacturing process, and reliable functional performance.
For engineers and procurement professionals, selecting PE coated paper requires more than checking basic GSM values. A thorough evaluation of coating thickness, heat seal performance, food safety documentation, and end-use conditions is essential to ensure long-term performance and regulatory compliance.
When used within its technical limits, PE coated paper remains one of the most practical and cost-effective functional paper materials available today.
